Programming Logic for Business
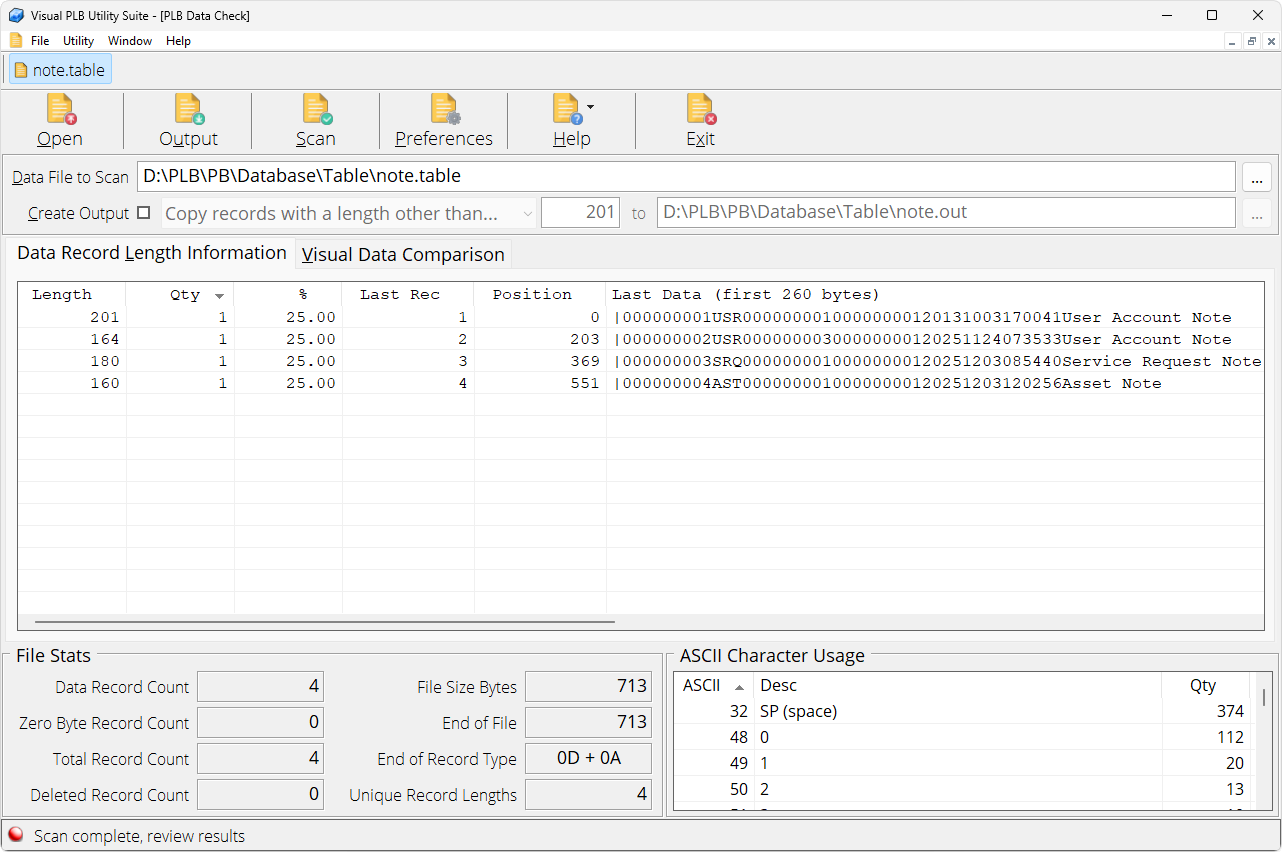
PLB Data Check
PLB Data Check is designed to scan a PLB data file and determine the individual data record lengths within the data file. Older MS-DOS command line program like pcDataCheck and fileStat had become a valuable tool within our collection of programmer utilities. However they were not compatible with 64-bit operating systems. PLB Data Check was designed to replace the basic functionality of those utilities, while utilizing the benefits of windows style program to make them easier to use as well as provide additional information.
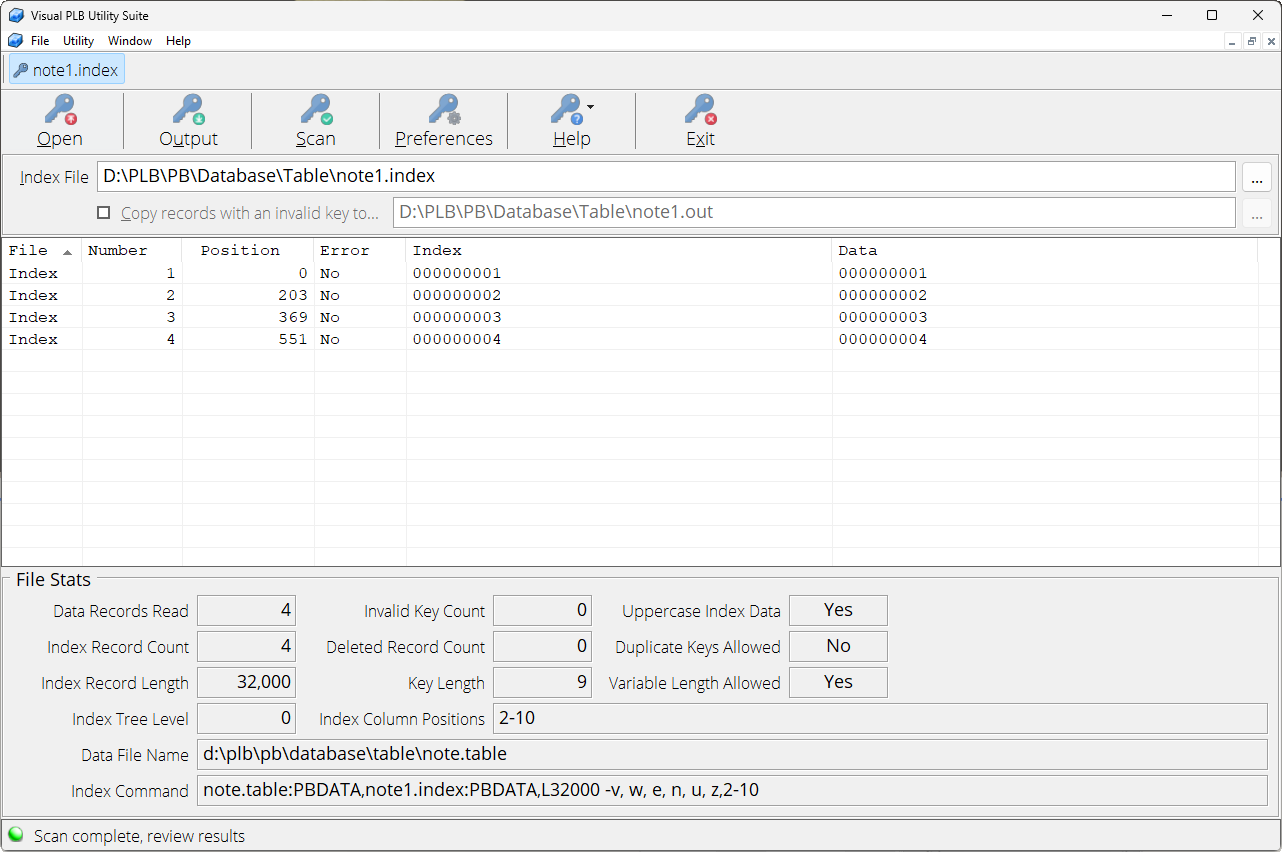
PLB Index Check
PLB Index Check is designed to scan a PLB ISAM index file and compare the internal index data to actual data within the associated PLB data file. If they don’t match, the results are displayed and can optionally be output to a file.
This utility can also be used as an index viewer. By changing a setting in the program preferences, the index and matching data for every record will be displayed/output. In this mode another column is added to the output that indicates if the record had an error or not.
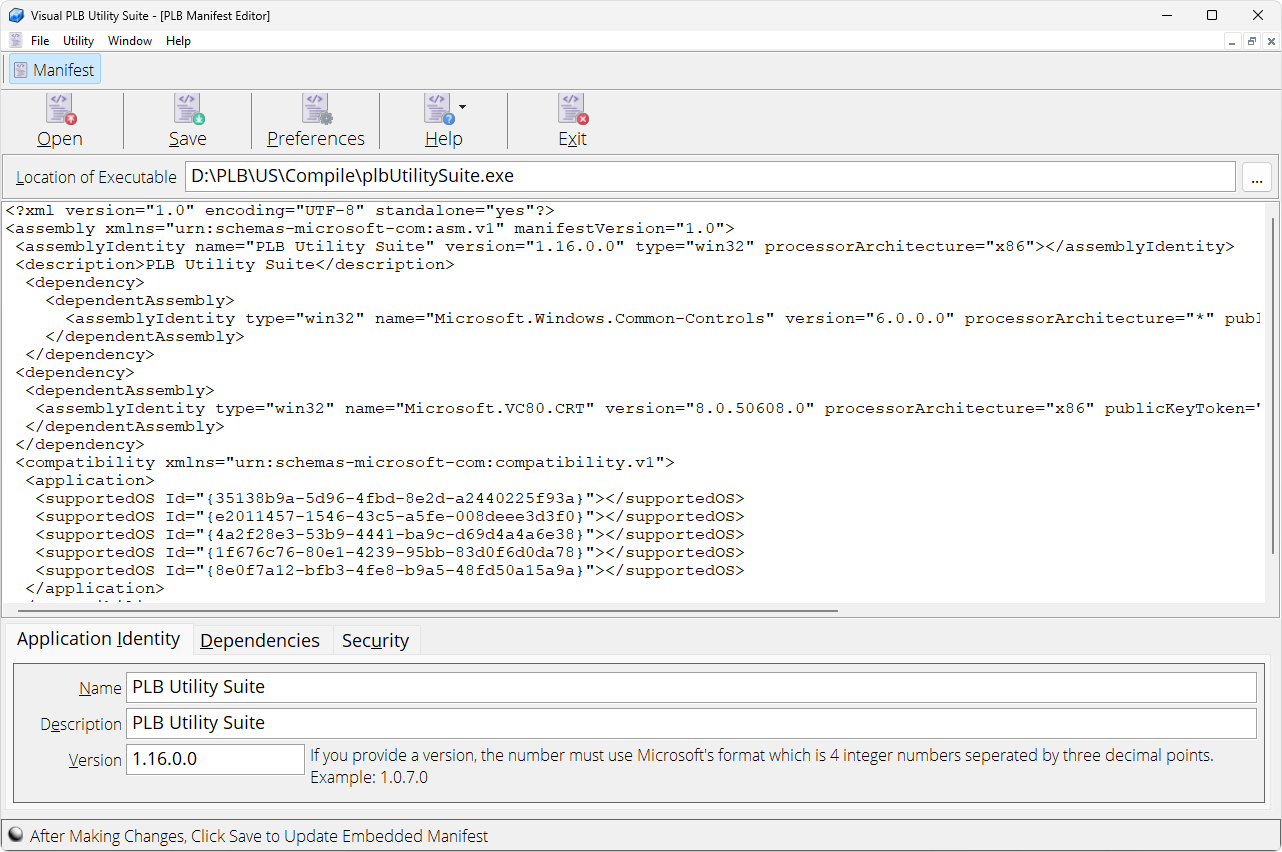
PLB Manifest Editor
A Windows “Manifest” is an XML file that is embedded within a Microsoft Windows executable file. When the operating system (XP or greater) loads the application and detects the presence of a manifest, the operating system’s DLL loader is directed to the specific version of the DLL that is listed in the manifest. If there is no manifest, the DLL loader loads a default version.
If you want a more detailed description of how a manifest file works, please read the following Wikipedia article.
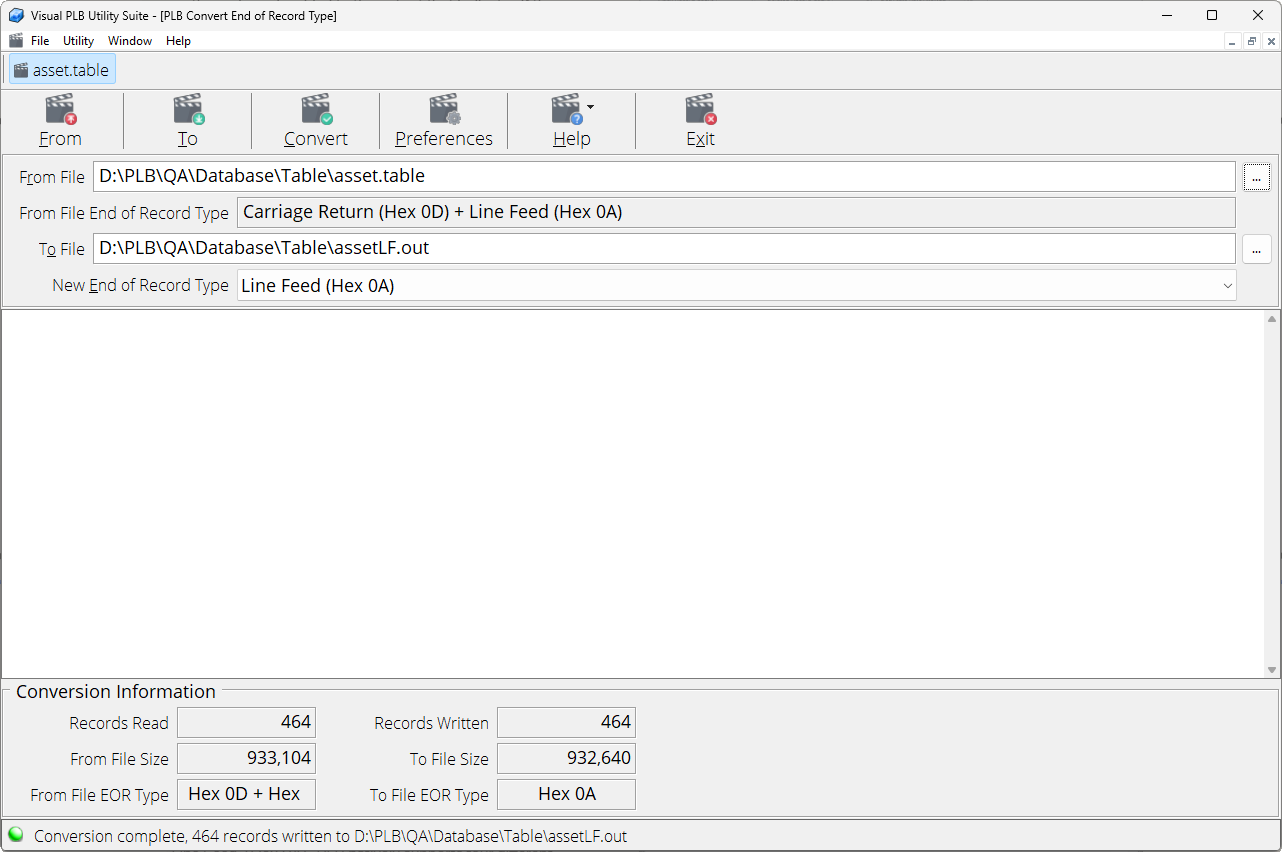
PLB Convert End of Record
Data files contain records, and individual records are separated within a data file by special “End of Record” ASCII control characters. The two specific ASCII control characters used are commonly referred to as the “Carriage Return” (Hex 0D) and “Line Feed” (Hex 0A). PLB natively supports four different types of “End of Record” formats, two of the formats use a single byte of data, and two of the formats use two bytes of data. The purpose of this program is to convert a data file from one type of End of Record format to another.
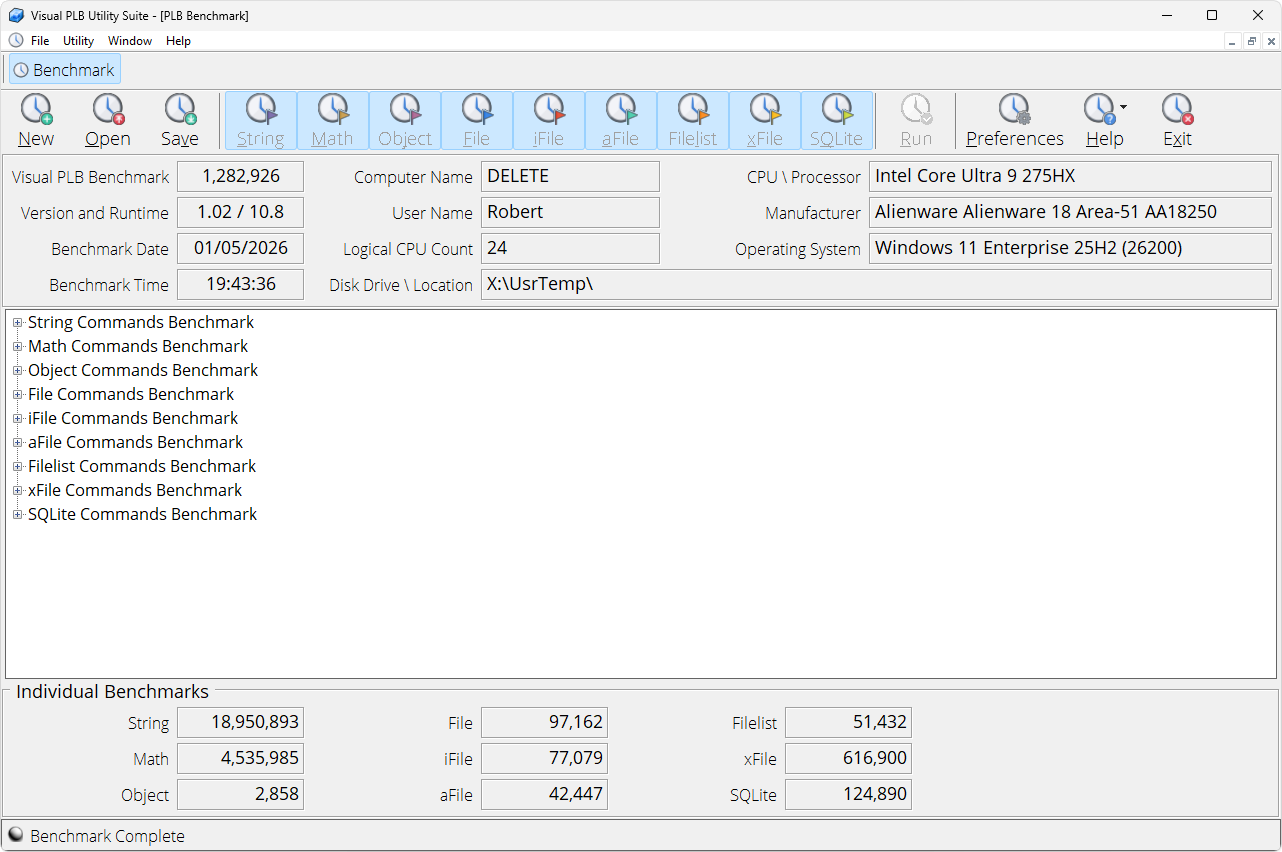
PLB Benchmark
The purpose of the PLB Benchmark utility is to provide a consistent performance measurement of PLB commands. PLB commands are grouped into eight categories (String, Math, Object, File, iFile, aFile, xFile, SQLite). Performance is measured in terms of instructions per second.